Neuralgia - A disease associated with damage to the peripheral nerves. Unlike neuritis, with neuralgia there are no structural changes in the affected nerve. The disease is characterized by severe pain in the area of innervation of the diseased nerve. Neuralgia usually develops in nerves that pass through narrow openings or canals.
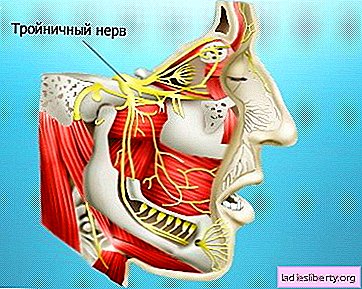
The most common type of neuralgia is the defeat of the trigeminal nerve (occurs as a result of facial injuries, dental diseases or malocclusion). The following species are also found:
- intercostal neuralgia (usually occurs after osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine);
- Neuralgia of the external cutaneous nerve of the thigh (pain of the outer surface of the thigh);
- Pterygo-neuralgia (occurs suddenly and is characterized by pain in the palate, eyes, temples and neck);
- neuralgia of the occipital nerve (pain in the neck, temples and eyes);
- glossopharyngeal nerve neuralgia (extremely rare, characterized by pain in the throat and lower jaw).
Neuralgia - causes
The disease is characterized by a variety of possible causes: trauma, the negative effects of heavy metals, the toxic effects of a number of bacteria and medicines, diseases of the nervous system (polyradiculoneuritis, sclerosis), infections (flu, tuberculosis), allergic reactions, spinal pathologies and others.
Neuralgia can be caused by diseases of the cardiovascular system (hypertension, anemia, atherosclerosis). The disease in this case is provoked by a weak influx of oxygen to the nerves. Neuralgia can also occur due to changes in the spine that occur during hormonal disorders in women during menopause.
Additional factors causing neuralgia can be alcohol abuse, diabetes mellitus, metabolic disorders involving vitamin B.
Neuralgia - Symptoms
The main symptom of neuralgia is characteristic pain. Attacks usually occur with hypothermia, with physical or emotional overstrain. Pain is often accompanied by a variety of autonomic disorders (edema of the skin, redness of the skin), in case of severe pain - by common vegetative-vascular manifestations. In patients with neuralgia, sensitivity disorders are revealed that manifest themselves in the form of hypesthesia or hyperesthesia. Often there are symptoms of tension of nerve trunks.
Neuralgia - diagnosis
The diagnosis of neuralgia of a nerve is usually based on the patient's complaints, as well as on data obtained by examination by a doctor. Quite often, neuralgia is diagnosed by exclusion, when as a result of numerous studies (general blood and urine tests, MRI, CT, etc.), it is not possible to identify the cause of the pain that the patient complains about.
Tingling, itching, burning, numbness, slight or severe pain are signs that may indicate localized neuropathic pain. In certain cases, it is characterized by persistent and constant painful sensations that are not removed by conventional analgesics. In the treatment of localized neuropathic pain, local action is considered preferable to eliminate pain, for which drugs have been developed that can cope with it in direct contact with the skin. Doctors often prescribe the modern drug Versatis - an anesthetic patch with lidocaine, which, when applied to a painful area of the skin, protects and pleasantly cools it, removing painful sensations of any intensity.
After diagnosis, it is recommended that magnetic resonance imaging is additionally used. This method will help to detect a tumor or a number of signs of sclerosis. However, other studies cannot determine other causes of neuralgia.
Neuralgia - treatment and prevention
Treatment for neuralgia can only be prescribed by a doctor. Therapy of primary neuralgia is complex and includes physiotherapeutic procedures, acupuncture, injections of novocaine and B vitamins.
Modern treatment for back pain has long gone from the simple elimination of discomfort. It is important to treat not the manifestations, but their cause. An example of such an integrated approach is the addition of NSAIDs with neurotropic vitamins (B1, B6, B12). B vitamins not only help to eliminate pain faster than taking NSAIDs (for example, diclofenac sodium), but also have a beneficial effect on physiological processes in the nerve fiber stimulate nutrition and restoration of the structure of nerve tissue.
So, the optimal complement to NSAIDs is Neuromultivit in injections, which includes three vitamins B1, B6, B12 in therapeutic dosages. The use of neurotropic vitamins in high therapeutic doses allows you to consolidate the analgesic effect, helps to restore nerve fiber, which helps to achieve long-term remission of the pain syndrome. They begin treatment with daily injections for 5-10 days, then switch to maintenance administration, 2-3 injections per week for two to three weeks.
In case of damage to the trigeminal nerve, anticonvulsants are used. The use of surgical intervention is not excluded.
With secondary (symptomatic) neuralgia, the main cause of the disease is identified, after which the doctor prescribes the necessary individual treatment.
Prevention of neuralgia involves:
- proper nutrition;
- rationality of physical activity;
- lack of hypothermia and injuries.
Comments
Girls! Have pity on yourself!
At the first signs of neuralgia, you need to see a doctor, then the treatment will be quick and effective.
Usually this happens: We do a full examination, prescribe NVPV (personally, I prefer Neurodiclovit as the most effective non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug) - this helps to cope with pain and stop inflammation, and then we make a decision depending on the neglect of the case and the type of neuralgia. Sometimes massage, or electrophoresis. Sometimes surgical intervention is required.
Take care of yourself, my dears!